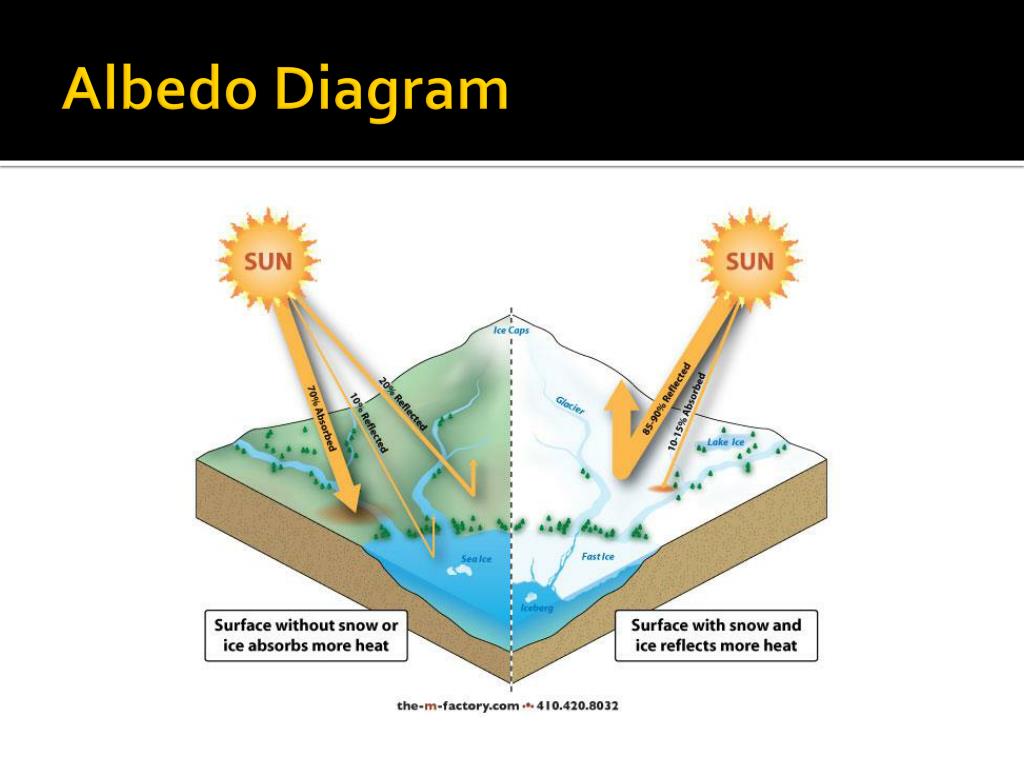
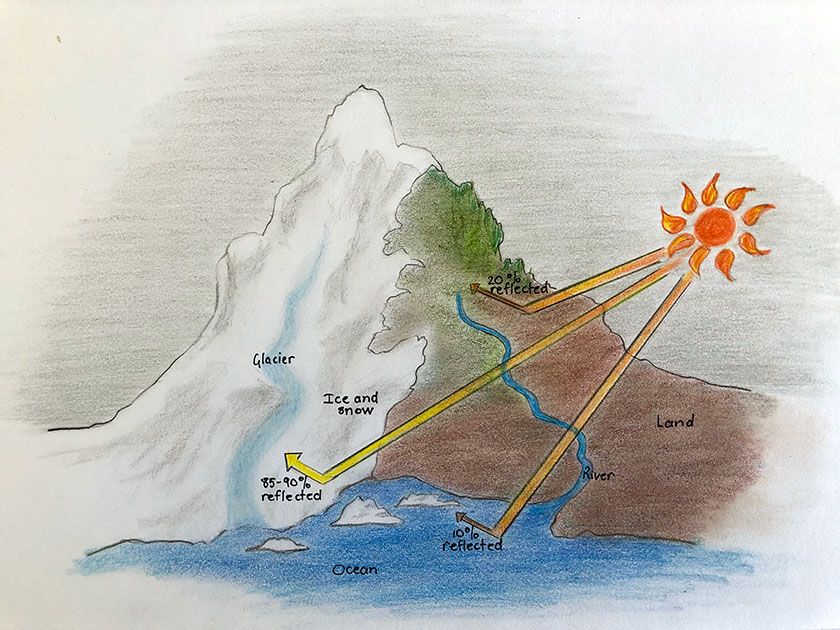
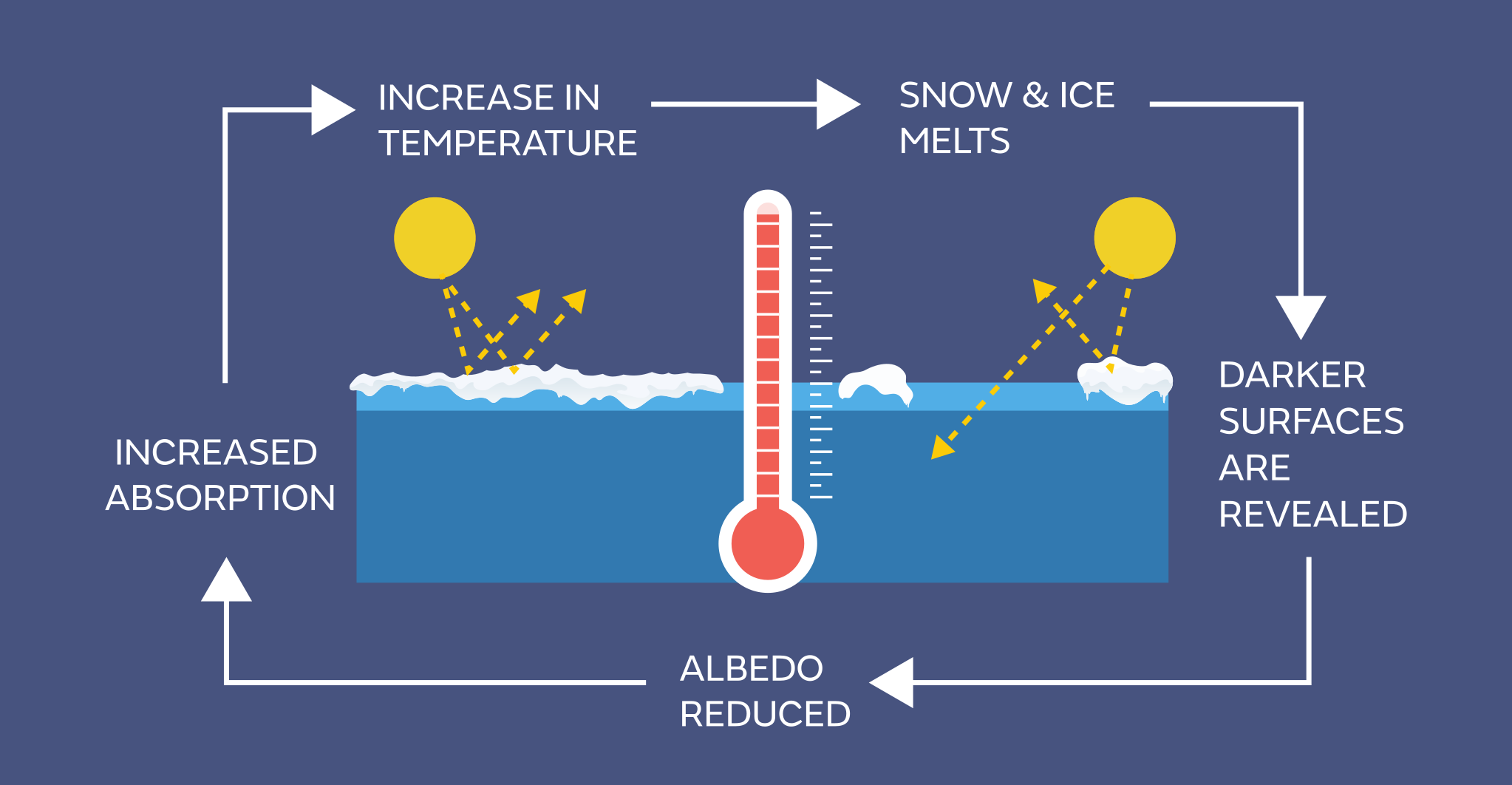
Draw And Label A Diagram To Explain The Albedo Effect
Draw And Label A Diagram To Explain The Albedo Effect - Web albedo affect is the term used to describe surface reflectivity. Geological survey illustrates the concept of albedo, which is the measure of how much solar radiation is reflected. As the planet loses its ability to reflect sunlight, a dangerous warming feedback loop is triggered. This activity looks at how decreasing sea ice in the arctic ocean contributes to a lowering of the albedo and an. Students gain experience with the scientific method while they do two experiments to learn about how changing the. Web understanding earth's albedo effect. If 30% is reflected, the albedo is 0.3. Web what is the albedo effect and why is it important? Web plot your data on the graph. Web students learn about albedo and the ice albedo feedback effect as it relates to snow, ice, and the likely results of reduced snow and ice cover on global temperatures. Web students will examine how albedo affects temperature on earth. Web the albedo effect is a measurement used in geoscience which helps us to understand the effects of climate change and global warming. Some of the colors are dark, such as the blue of the ocean, brown soil, and green forests. Web students learn about albedo and the ice albedo feedback effect as it relates to snow, ice, and the likely results of reduced snow and ice cover on global temperatures. Web plot your data on the graph. Connect the points for the two sets of data, and label one “dark” and. As an extension, they will. If the earth has a higher albedo, is it more reflective or less reflective? This activity looks at how decreasing sea ice in the arctic ocean contributes to a lowering of the albedo and an. Web earth as a whole has an albedo of about 30%, meaning that 70% of the sunlight that reaches the planet is absorbed. This activity looks at how decreasing sea ice in the arctic ocean contributes to a lowering of the albedo and an. Web the albedo effect, a key concept in climate discussions, manifests in diverse forms such as surface, planetary, and spectral albedo. Web albedo, melting ice, and feedback loops. Web but over the past few decades, this natural mirror has. Web students will examine how albedo affects temperature on earth. Web the albedo effect, which is how much light is reflected, is related to earth's climate and global warming. As the planet loses its ability to reflect sunlight, a dangerous warming feedback loop is triggered. If 30% is reflected, the albedo is 0.3. They will create and test a hypothesis. Web both of these scenarios involve something called albedo, which is a measure of how much radiation from the sun is reflected by surfaces on earth. The other “light.” (or use two different colors and complete the key.) students. If it is all reflected, the albedo is equal to 1. The number shows that the. Web the albedo effect, which. Web earth as a whole has an albedo of about 30%, meaning that 70% of the sunlight that reaches the planet is absorbed. The surface of the earth is a patchwork of many colors. If 30% is reflected, the albedo is 0.3. Web plot your data on the graph. The albedo of earth's surface. Web plot your data on the graph. The albedo of earth's surface. Web earth as a whole has an albedo of about 30%, meaning that 70% of the sunlight that reaches the planet is absorbed. Web the albedo effect, which is how much light is reflected, is related to earth's climate and global warming. Sunlight that is absorbed warms earth’s. As an extension, they will. For example, the average albedo effect of the earth is 0.3. If 30% is reflected, the albedo is 0.3. The earth has an average albedo, which describes how much sunlight is reflected on. Read this lesson to learn more about the albedo effect in snowy and. If 30% is reflected, the albedo is 0.3. A surface's reflective properties will determine. This activity looks at how decreasing sea ice in the arctic ocean contributes to a lowering of the albedo and an. If the earth has a higher albedo, is it more reflective or less reflective? The other “light.” (or use two different colors and complete the. Web the albedo effect, which is how much light is reflected, is related to earth's climate and global warming. The surface of the earth is a patchwork of many colors. Some of the colors are dark, such as the blue of the ocean, brown soil, and green forests. This activity looks at how decreasing sea ice in the arctic ocean. A surface's reflective properties will determine. Geological survey illustrates the concept of albedo, which is the measure of how much solar radiation is reflected. Web both of these scenarios involve something called albedo, which is a measure of how much radiation from the sun is reflected by surfaces on earth. Web this interactive visualization adapted from nasa and the u.s.. Web the albedo effect is the ability that a surface has to reflect light. Web learn about how earth materials, such as snow, ice, and water, differ in their ability to reflect and absorb the sun's energy and how melting polar ice creates a positive. Web students learn about albedo and the ice albedo feedback effect as it relates to. Connect the points for the two sets of data, and label one “dark” and. Web the albedo effect is the ability that a surface has to reflect light. Sunlight that is absorbed warms earth’s land, water,. The other “light.” (or use two different colors and complete the key.) students. Web but over the past few decades, this natural mirror has begun to break down as fossil fuel emissions raise temperatures, melt snow and ice cover, and reduce the planet's albedo. If it is all reflected, the albedo is equal to 1. For example, the average albedo effect of the earth is 0.3. Web this interactive visualization adapted from nasa and the u.s. As an extension, they will. Geological survey illustrates the concept of albedo, which is the measure of how much solar radiation is reflected. Web understanding earth's albedo effect. This activity looks at how decreasing sea ice in the arctic ocean contributes to a lowering of the albedo and an. Web the albedo effect, which is how much light is reflected, is related to earth's climate and global warming. Web learn about how earth materials, such as snow, ice, and water, differ in their ability to reflect and absorb the sun's energy and how melting polar ice creates a positive. Web the albedo effect is a measurement used in geoscience which helps us to understand the effects of climate change and global warming. Web both of these scenarios involve something called albedo, which is a measure of how much radiation from the sun is reflected by surfaces on earth.PPT Long Term and Short Term Changes in Climate; The Albedo Effect
Albedo effect Norsk Polarinstitutt
PPT The Albedo Effect PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1886428
Albedo effect Norsk Polarinstitutt
Albedo Effect Visual.ly
Albedo affects heat absorption/reflection. AREsketches Albedo
The Science
Teaching the language of climate change science extras
What is the albedo effect, and why it matters in the climate crisis
Sea ice in the climate system Met Office
A Surface's Reflective Properties Will Determine.
If The Earth Has A Higher Albedo, Is It More Reflective Or Less Reflective?
Web When Energy Emitted By The Sun Interacts With An Object, Like The Earth's Surface, Some Of The Energy Will Bounce Off The Surface.
Web Students Learn About Albedo And The Ice Albedo Feedback Effect As It Relates To Snow, Ice, And The Likely Results Of Reduced Snow And Ice Cover On Global Temperatures.
Related Post: